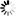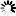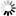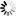| View | Docbook | HTML |
|---|---|---|
|
.  |
|
|
Figure 737. A MathML equation 

| View | Docbook | HTML |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Figure 738. A TeX equation 

| Docbook | HTML |
|---|---|
|
|
|
$ |x| = \left\{ \begin{array}{rl} -x
&\mbox{if $x<0$} \\ x &\mbox{otherwise}
\end{array} \right.$
|
|
See Formal elements.